How to Estimate the Total Cost of Building a Website is an essential guide for anyone looking to embark on the journey of creating a website. Understanding the various financial aspects before diving into a project can save time, resources, and unexpected challenges. By exploring the myriad factors that influence website costs—from design and development to hosting and ongoing maintenance—this article aims to equip readers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions in their web-building endeavors.
The discussion will delve into critical cost components, statistical insights from different industries, and practical budgeting strategies that can significantly impact the success of a website project. By analyzing real-life examples and case studies, we will highlight the importance of thorough cost estimation and the implications of design and development choices on overall expenses.
Introduction to Website Building Costs
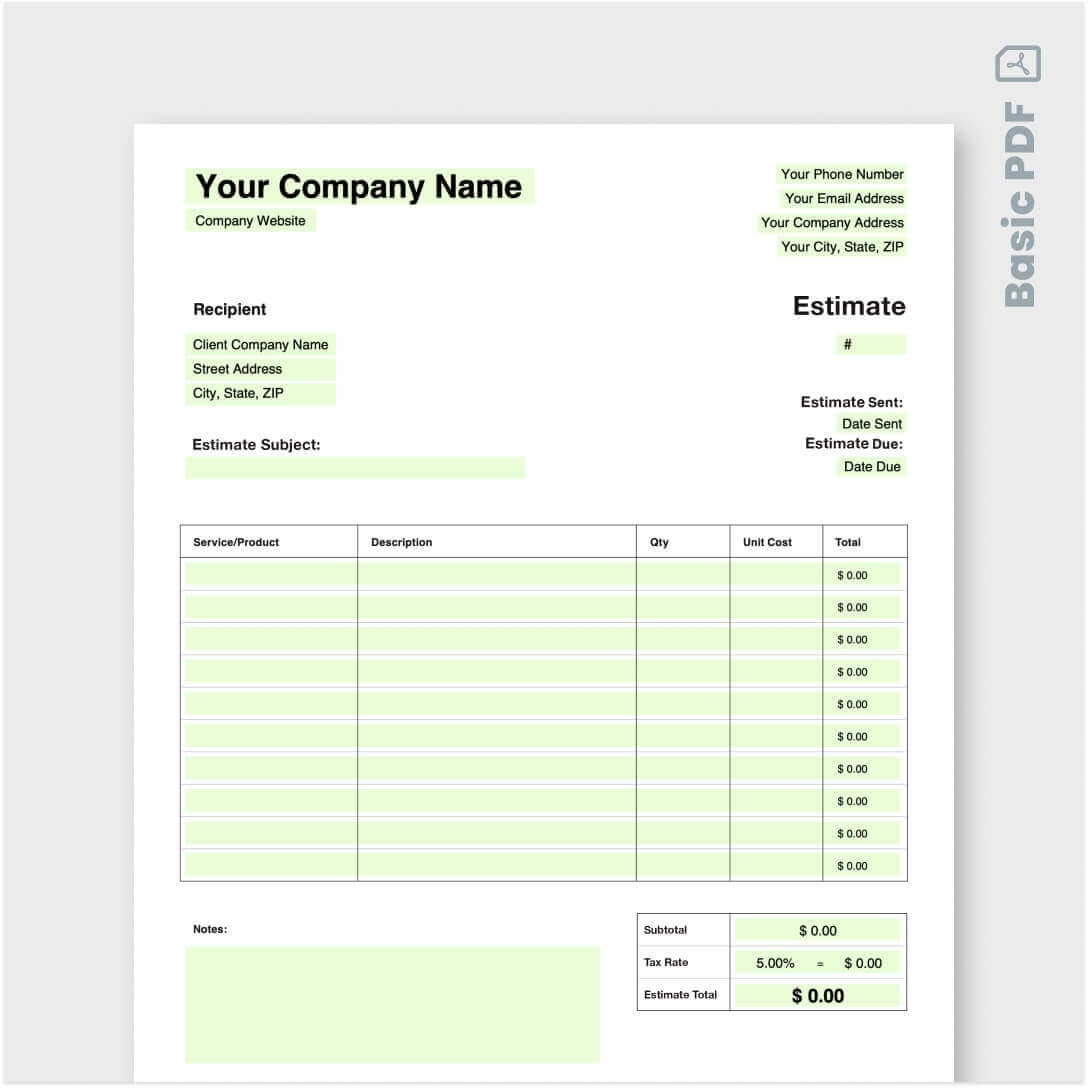
Estimating the costs involved in building a website is a critical step that can significantly influence the success of any online venture. A comprehensive understanding of these costs allows businesses and individuals to allocate their budgets effectively and make informed decisions throughout the development process. Without a clear estimation, projects may face unexpected financial hurdles that can derail their objectives.There are several factors that influence the overall costs of creating a website.
These variables range from the complexity of the design, the functionality required, the choice of platform, and ongoing maintenance needs to domain registration and hosting fees. Additionally, the industry in which a business operates can also have a substantial impact on website costs, as different sectors have varying requirements and standards for online presence.
Factors Influencing Website Costs
Understanding the components that contribute to website costs is essential for anyone looking to build an effective online presence. The following elements are some of the most significant contributors to the total expenditure:
- Design Complexity: The intricacy of the website’s layout and aesthetics directly affects cost. Custom designs typically require more investment compared to template-based solutions.
- Functionality Requirements: Features such as e-commerce capabilities, user registration, and payment gateways can increase costs due to the additional development work involved.
- Content Management System (CMS): The choice of CMS impacts costs, with platforms like WordPress being more budget-friendly compared to bespoke solutions.
- Hosting and Domain Costs: Selecting a reliable hosting service and acquiring a domain name are foundational expenses that affect the overall budget.
- and Marketing: Investments in Search Engine Optimization () and advertising are crucial for visibility and can vary widely based on the chosen strategies.
The average cost of building a website can vary significantly across industries. For instance, a basic informational website might cost anywhere from $1,000 to $5,000, whereas e-commerce sites can range from $5,000 to upwards of $50,000 depending on the features required. According to recent data, the average small business website costs around $3,000, while industry-specific websites might demand more depending on regulatory compliance and specialized functionalities.
“Budgeting for a website is not just about the upfront costs; ongoing maintenance and upgrades should also be factored into total expenses.”
The importance of correctly estimating website building costs cannot be overstated. A detailed understanding of these expenses helps in outlining a realistic budget, minimizing the risk of overspending, and ensuring that the website serves its intended purpose effectively. By evaluating all the factors influencing costs, businesses can better prepare for the financial commitment involved in establishing their online presence.
Identifying Key Cost Components
When embarking on the journey of building a website, it is essential to understand the various cost components involved. A comprehensive overview helps in budgeting accurately and avoiding unexpected expenses. Each element plays a critical role in the overall expenditure, and knowing these can lead to better decision-making throughout the website development process.The primary components that contribute to the total cost of a website include design, development, hosting, and maintenance.
Each of these elements has distinct implications for the final price and must be carefully considered to ensure a successful web project.
Cost Components Overview
Understanding the cost components of a website is crucial for effective budgeting and planning. The following table Artikels typical cost ranges associated with each component, offering insights into their significance:
| Component | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Website Design | $1,000 – $10,000 |
| Website Development | $2,000 – $20,000 |
| Hosting Services | $100 – $500 per year |
| Maintenance | $500 – $5,000 per year |
### Website DesignThe design of a website is often the first interaction a user has with it; hence, it is a vital component that influences user experience. The cost for design can vary based on the complexity, customization, and the designer’s expertise. A basic design could cost around $1,000, while a more elaborate, custom design may reach up to $10,000 or more.
Investing in professional design ensures a visually appealing website that aligns with business branding.### Website DevelopmentWebsite development encompasses the technical aspects of building a site, including coding, functionality, and the integration of various systems. This component usually represents a significant portion of the budget, ranging from $2,000 to $20,000. The final cost depends on the complexity of the project, the technology stack chosen, and whether the site requires custom features or e-commerce capabilities.### Hosting ServicesHosting is the service that makes a website accessible on the internet.
The costs associated with hosting can vary based on the type of hosting (shared, VPS, dedicated) and the level of service provided. Typically, hosting services range from $100 to $500 annually. Reliable hosting is crucial as it affects site performance, uptime, and overall user experience, making it a key consideration in the budgeting process.### MaintenancePost-launch, websites require ongoing maintenance to ensure they function correctly and remain secure.
This encompasses updates, backups, troubleshooting, and content management. Maintenance costs generally range from $500 to $5,000 per year, depending on the website’s complexity and the level of service required. Regular maintenance is essential to keep the website relevant and operational, which ultimately contributes to its overall success.In summary, recognizing the key components of website costs is vital for effective planning and management of resources.
Each element not only contributes to the overall expenditure but also plays a significant role in the functionality and success of the website.
Design Costs
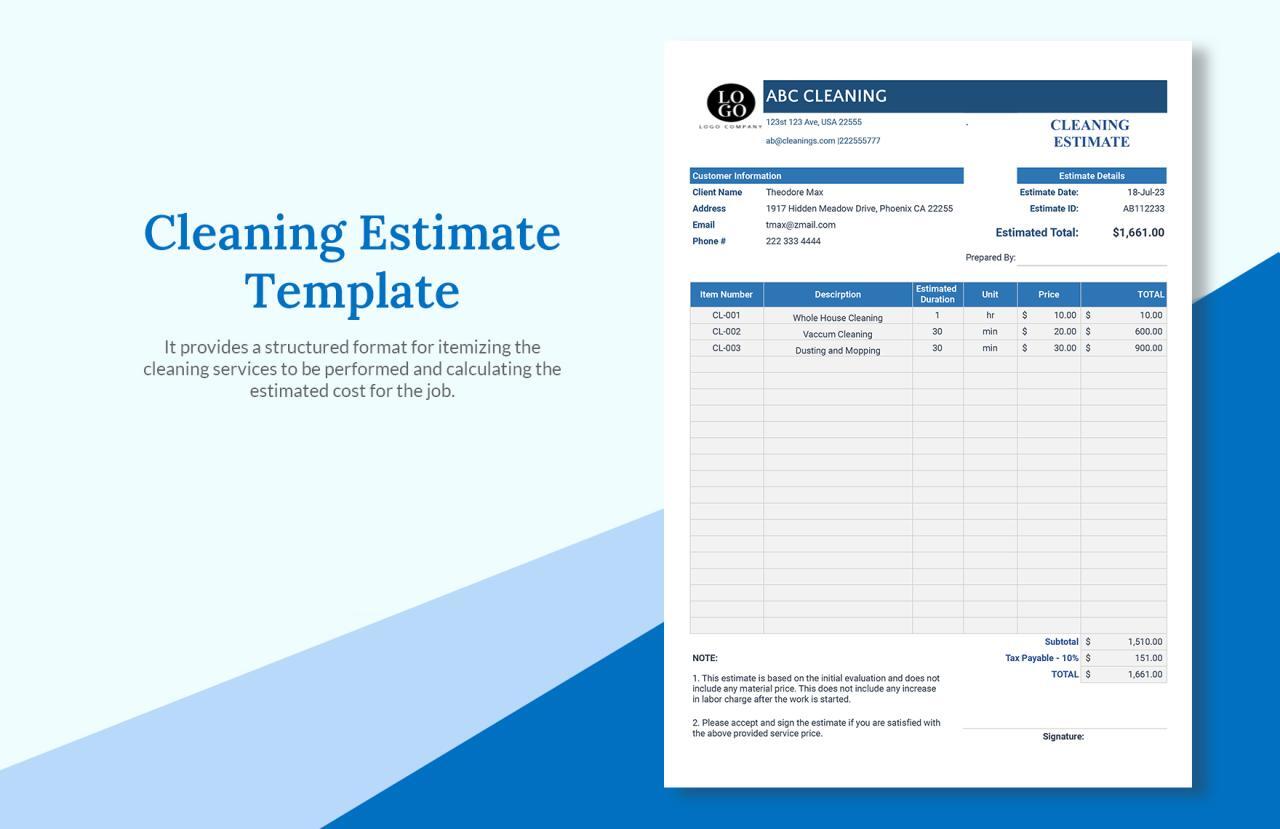
The design of a website plays a critical role in determining its overall cost. Factors such as design complexity, customization level, and the choice between templates and custom designs significantly influence financial investment. It is essential to understand how these design choices impact not only the visual appeal but also the functionality and user experience of the site.Design choices can broadly be divided into two categories: templates and custom designs.
Templates are pre-designed layouts that can be modified to suit specific needs, typically at a lower cost. On the other hand, custom designs are tailored to the client’s specifications, offering unique features but often at a higher expense. Below is a breakdown of the associated costs for different design options:
Cost Breakdown of Design Elements
The financial implications of design can be categorized into several components, each contributing to the overall expenditure. Understanding these components assists in making informed decisions regarding budget allocation for website design.
- Graphic Design: This includes the creation of visual elements such as logos, icons, and images. Professional graphic design can range from $500 to $5,000 depending on the complexity and the designer’s experience.
- UI/UX Design: User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) design focus on optimizing the interaction between users and the website. The costs for professional UI/UX design services can vary between $1,000 to $10,000, depending on the scope of the project and the level of research and testing involved.
- Animations: Incorporating animations can greatly enhance user engagement. Simple animations may cost around $300 to $1,500, while more complex animations requiring advanced skills may reach upwards of $5,000.
Custom designs often yield a higher return on investment due to their ability to create a distinct brand identity and enhance user experience.
In summary, understanding the cost implications of design choices is crucial for budgeting effectively when building a website. The right balance between aesthetic appeal and functional design will ultimately contribute to the website’s success in achieving business goals.
Development Costs
Estimating development costs is crucial for a successful website project. These costs can vary significantly based on the development approach, the complexity of features, and the location of the development team. Understanding these factors will enable businesses to allocate their budget effectively while ensuring the desired quality and functionality.There are primarily two development approaches: custom development and using Content Management System (CMS) platforms.
Custom development offers tailored solutions, allowing for unique features and designs. However, it often comes at a higher price due to the extensive coding and design work required. On the other hand, CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal offer pre-built templates and plugins, which generally reduce development time and costs, making them an attractive option for many businesses.
Comparison of Front-End and Back-End Development Costs
Both front-end and back-end development play critical roles in website creation, and their costs can differ based on various factors. Front-end development focuses on the visual aspects of a website, such as layout, design, and interactivity, using languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This often involves a high level of creativity and user experience design, which can influence the overall cost.Back-end development, however, relates to server-side operations, databases, and application logic.
This typically requires more technical expertise and understanding of server management, API integrations, and data processing. While the complexity of features significantly impacts costs for both areas, back-end development tends to be more expensive due to the intricate skill set required.To provide a clearer understanding of the costs associated with web development, the following table illustrates average hourly rates for web developers across different regions:
| Region | Average Hourly Rate (USD) |
|---|---|
| North America | $100 – $150 |
| Western Europe | $70 – $120 |
| Eastern Europe | $30 – $70 |
| Asia | $20 – $50 |
| South America | $25 – $60 |
These figures serve as a benchmark for estimating costs based on geographical location. It is essential to consider not only the rates but also the expertise and quality of work provided by developers in each region.
Hosting and Domain Costs
When building a website, understanding hosting and domain costs is crucial for budgeting effectively. These costs not only affect your initial investment but also have ongoing financial implications that can influence your website’s performance and accessibility. This section will break down the various hosting options available, the fees associated with domain registration, and a comparative analysis of popular hosting providers.
Types of Hosting Services
There are several types of hosting services, each with different features and price points. Understanding these options will help you select the best fit for your website’s needs and budget.
- Shared Hosting: This is the most economical option, where multiple websites share a single server’s resources. It’s suitable for small websites and blogs with low traffic. Prices typically range from $3 to $10 per month.
- Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting: VPS hosting offers more resources and flexibility than shared hosting, as it partitions a server into virtual servers. This type is ideal for growing websites needing more control and performance, with costs ranging from $20 to $100 per month.
- Dedicated Hosting: In dedicated hosting, an entire server is rented for a single website, providing maximum control and resources. This option is optimal for high-traffic sites or those requiring specific server configurations, with prices usually starting from $80 and going up to several hundred dollars per month.
Domain Registration Fees
Securing a domain name is a fundamental step in establishing your website. Domain registration typically involves both initial registration fees and renewal costs, which are essential to keep your domain active.The average cost for domain registration can vary based on the domain extension (.com, .org, .net, etc.) and the registrar chosen. Generally, you can expect to pay between $10 and $20 per year for most domain names.
Renewal fees are typically similar to the registration costs, although some registrars may offer discounts for multi-year registrations.
Comparison of Popular Hosting Providers
Evaluating various hosting providers can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and requirements. Below is a comparison chart of some well-known hosting providers and their pricing structures.
| Provider | Type of Hosting | Starting Price (per month) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bluehost | Shared | $2.95 | Free domain for the first year, 24/7 support, and SSL certificate. |
| SiteGround | Shared | $3.99 | High-performance servers, daily backups, and excellent customer service. |
| HostGator | VPS | $19.95 | Scalable resources, dedicated IP, and full root access. |
| DigitalOcean | VPS | $5.00 | Cloud infrastructure, flexible scaling, and developer-friendly tools. |
| InMotion Hosting | Dedicated | $99.99 | Free SSDs, high reliability, and 90-day money-back guarantee. |
“The choice of hosting and domain registration is foundational to your website’s success, impacting both site performance and long-term viability.”
Additional Features and Functionality
When building a website, the inclusion of additional features and functionality is a crucial aspect that can significantly influence both the user experience and the overall costs. These features often extend the capabilities of a website, enhancing its usability, performance, and visitor engagement. Understanding the associated costs of these features is essential for effective budget planning and optimal resource allocation.The costs for adding specific features such as e-commerce capabilities, tools, and content management systems can vary widely based on complexity and the specific technologies used.
Each of these functionalities not only requires development time but may also necessitate ongoing maintenance and updates. The integration of third-party services can add additional expenses but can also provide significant value by enhancing functionality without the need for extensive in-house development.
E-commerce Capabilities
E-commerce functionality is vital for any website intending to sell products or services online. This feature typically involves costs related to setting up shopping carts, payment gateways, inventory management systems, and security measures for processing transactions. The average costs associated with e-commerce solutions range from $2,000 to $10,000 or more, depending on the complexity of the system and the number of products being offered.
Tools
Search Engine Optimization () tools are essential for enhancing a website’s visibility on search engines. Implementation costs for features can include research tools, analytics, and optimization plugins. The investment in these tools can range from $500 to $3,000, depending on whether they are integrated into existing systems or built from scratch.
Content Management Systems
A Content Management System (CMS) allows users to create, manage, and modify content on a website without needing specialized technical knowledge. The costs associated with implementing a CMS can vary significantly; popular platforms such as WordPress or Joomla may incur fees ranging from $1,000 to $5,000, depending on customization needs and additional plugins.
Third-Party Integrations
Integrating third-party services can enhance the functionality of a website significantly. Examples include marketing automation tools, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and social media platforms. The costs related to these integrations can vary based on the service provider and complexity but typically range from $500 to $5,000.
Common Features and Their Average Costs
Understanding the average costs associated with common features can help in budgeting effectively for website development. Below is a comprehensive list of these features along with their estimated costs:
| Feature | Average Cost |
|---|---|
| E-commerce Integration | $2,000 – $10,000 |
| Tools | $500 – $3,000 |
| Content Management System | $1,000 – $5,000 |
| Payment Gateway Integration | $500 – $2,500 |
| Social Media Integration | $200 – $1,000 |
| Email Marketing Integration | $300 – $2,000 |
| Analytics Tools | $100 – $1,500 |
Maintenance and Ongoing Costs
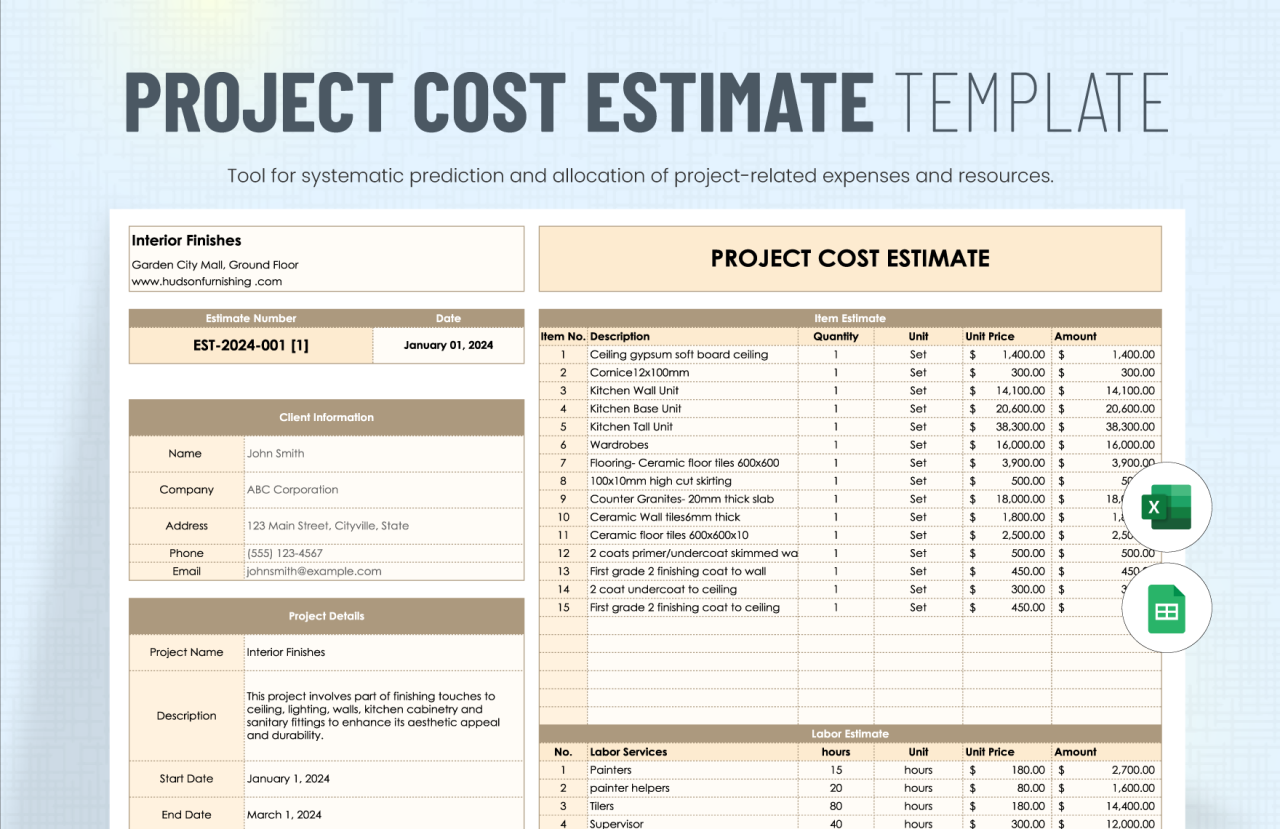
Budgeting for ongoing maintenance and updates is a crucial aspect of website ownership. Websites require continuous attention to remain functional, secure, and relevant to users. Regular updates not only enhance the user experience but also improve search engine rankings, making it essential to set aside resources for these expenses.Ongoing costs primarily encompass content updates, security measures, and technical support. Without adequate budgeting in these areas, a website can quickly fall behind in performance, leading to potential security threats and decreased user engagement.
Understanding these costs can help in creating a sustainable financial plan for website management.
Content Updates and Security Costs
Content updates are essential for keeping a website fresh and engaging. They contribute to search engine optimization () and provide visitors with valuable information. The costs associated with content updates can vary considerably based on the frequency and type of updates required. A blog or news site may necessitate updates several times a week, while a portfolio website may only require occasional changes.Security is another vital aspect of website maintenance.
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, making it essential to invest in robust security measures, including regular software updates, SSL certificates, and firewall protection. The annual costs for these components can typically range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the complexity and scale of the site.To estimate annual maintenance costs effectively, consider the following strategies:
- Assess the website’s current state and identify areas needing regular updates.
- Evaluate the frequency of expected content updates and the associated labor costs.
- Determine necessary security measures based on the website’s nature and the potential risk factors involved.
- Factor in technical support costs, which may include hiring specialists for troubleshooting or site-specific needs.
By carefully evaluating these elements, website owners can create a comprehensive plan that allows for effective maintenance while ensuring the site remains competitive and secure.
Estimating Annual Maintenance Costs
Estimating annual maintenance costs can vary significantly based on the type of website in question. For example, e-commerce sites may require more frequent security updates and content changes due to the nature of online transactions. Conversely, a static informational website may have lower ongoing costs. A general approach to estimate these costs includes:
- For a simple website, budget around $300 to $600 annually for basic updates and maintenance.
- For a blog or content-driven site, anticipate costs between $600 and $1,200 annually, considering regular content creation and efforts.
- E-commerce websites often incur higher costs, ranging from $1,200 to $5,000 annually, given the need for enhanced security and frequent content updates.
By using these estimates as guidelines, businesses can allocate the appropriate budget to ensure their website remains functional, secure, and engaging for users.
“Planning for maintenance is as important as the initial investment in building a website.”
Creating a Budget
Creating a budget for a website project is essential for ensuring that all costs are accounted for and that the project remains financially feasible. A well-structured budget allows for effective allocation of resources, minimizing the risk of unexpected expenses that could derail the project. It serves as a financial blueprint that guides all stages of the website development process.To establish a comprehensive budget, it is important to break down the costs associated with each component identified earlier in the project.
This involves estimating the costs based on various factors, including design, development, hosting, and ongoing maintenance. Below is a step-by-step guide for estimating costs based on the identified components.
Step-by-Step Guide for Estimating Costs
The following steps can be taken to estimate costs effectively:
1. List All Identified Components
Begin by compiling all the cost components identified in previous sections, such as design, development, hosting, and any additional features.
2. Research Costs
Conduct research to determine current market rates for each component. This may include consulting service providers, comparing packages, or analyzing competitors’ pricing strategies.
3. Estimate Resource Allocation
Identify the resources required for each component, including personnel, tools, and technologies. Estimate the time needed for each task and assign costs accordingly.
4. Consider Contingency Funds
Always allocate a percentage of the total budget for unforeseen expenses. A common practice is to set aside 10-20% of the total budget as a contingency fund.
5. Prepare the Budget Template
Utilize a budget template to organize the estimated costs clearly. This can be an Excel spreadsheet or a project management tool that allows for easy adjustments.
6. Review and Adjust
Once the initial budget is prepared, review it with stakeholders. Gather feedback, adjust estimates as necessary, and ensure all perspectives are considered.
Examples of Budget Templates for Web Development Projects
Utilizing a budget template can greatly assist in the tracking and management of website development costs. Here are a few examples of budget templates that can be employed:
1. Excel Budget Template
A simple Excel spreadsheet with columns for components, estimated costs, actual costs, and variances. This allows for easy updates and modifications throughout the project.
2. Google Sheets Budget Template
Similar to the Excel template, a Google Sheets version allows for real-time collaboration and sharing with team members and stakeholders, enhancing transparency.
3. Project Management Software
Tools like Trello, Asana, or Monday.com often come with built-in budgeting features. These platforms offer the ability to create tasks with cost estimates and track spending dynamically.
4. Custom Budget Tracking Tools
There are specialized tools designed for web projects, such as FunctionFox or Harvest, which provide more advanced budgeting options, including time tracking and invoicing.By employing a structured approach to budgeting, website projects can significantly improve their financial management, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and that the project remains on track to meet its financial goals.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples

Understanding the various factors influencing website costs can be greatly enhanced by examining real-life case studies from different businesses. These examples illustrate how diverse requirements, design choices, and additional features can impact the total cost of building a website. By analyzing these cases, we can draw valuable lessons that can guide future projects and budgeting strategies.
Case Study: E-commerce Store
A mid-sized e-commerce retailer, specializing in handmade crafts, invested approximately $25,000 in their website. This cost included unique designs, robust development for e-commerce functionality, and secure payment processing systems. Key factors contributing to their overall expense included the need for high-quality product images, custom branding, and an integrated inventory management system.The following points summarize the lessons learned from this case study:
- Investing in quality design and user experience significantly enhances customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
- Integrating essential e-commerce functionalities early in the project can prevent costly adjustments later.
- Regularly updating product images and descriptions is vital for keeping the site engaging.
Case Study: Non-Profit Organization
A non-profit focused on environmental conservation allocated around $10,000 for their website. This budget predominantly covered basic design and content management system (CMS) setup, allowing them to easily update their information. Their limited budget resulted from relying on volunteer developers and using pre-existing templates.Key insights derived from this case include:
- Utilizing templates can significantly reduce costs while still delivering a professional look.
- Engaging volunteers or skilled board members for development tasks can help manage expenses effectively.
- Clear messaging and calls to action are crucial for non-profit websites to drive donations and support.
Case Study: Corporate Website Redesign
A large corporation decided to redesign their website, investing around $100,000. The comprehensive project involved extensive custom development, intricate data management features, and an elaborate UX/UI design process. Factors such as the need for high-level security features and integration with other corporate systems contributed to the higher cost.The lessons from this transformation include:
- High-level security is essential for corporate websites, especially those handling sensitive information.
- Collaboration between departments can yield a more functional website tailored to both customer and employee needs.
- Investing in research and testing during the design phase can lead to more informed decisions and better user engagement.
Case Study: Personal Blog
An individual blogger spent approximately $3,000 to create a personal blog focused on travel experiences. This cost primarily covered hosting, domain registration, and basic design. The blogger opted for minimal features and relied on content-driven strategies, which kept expenses low.Insights from this case study highlight:
- Focusing on content quality over extensive features can be a cost-effective approach for personal projects.
- Choosing affordable hosting options can help maintain a lower budget while still achieving decent performance.
- Engaging with an audience through authentic storytelling can yield strong organic traffic without hefty marketing costs.
Conclusion and Next Steps

After estimating the total cost of building a website, it is crucial to Artikel the next steps to ensure a successful project execution. Identifying a suitable developer or agency is essential as they will bring your online vision to life. With a clear understanding of your budget, you can now approach potential partners with confidence, ensuring that your financial expectations align with their capabilities.Selecting the right developer or agency involves evaluating their previous work, understanding their pricing structure, and assessing their communication style.
A well-defined budget not only aids in selecting capable professionals but also sets a solid foundation for the project. It is important to remain flexible and revisit budget estimates as the project evolves, as unforeseen factors may arise that influence costs.
Revisiting Budget Estimates
Budget estimates should be treated as a living document throughout the website development process. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your budget allows for better financial management and ensures the project stays on track. Factors such as scope changes, additional features, or delays can necessitate budget revisions. By actively monitoring expenses and comparing them to your initial estimates, you can make informed decisions and pivot as needed.
Communicating Budget Constraints
Effectively communicating your budget constraints to developers is vital for maintaining transparency and fostering a collaborative environment. Here are several tips to facilitate this process:
- Be Clear and Direct: Clearly articulate your budget limits from the outset to avoid misunderstandings later.
- Prioritize Features: Identify which features are essential and which can be considered optional, allowing for flexibility in negotiations.
- Encourage Open Dialogue: Foster an environment where developers feel comfortable discussing potential cost implications and alternatives.
- Request Estimates Regularly: Ask for budget updates at various stages of the project to ensure alignment and address any concerns promptly.
- Document Everything: Keep a written record of your budget discussions and agreements to reference throughout the project.
By following these steps, you will be better equipped to manage your website project effectively, ensuring that it meets both your functional needs and budgetary constraints. The success of your website development venture relies not only on accurate cost estimation but also on maintaining open lines of communication with your development team.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, estimating the total cost of building a website is a crucial step that sets the foundation for a successful online presence. By considering all necessary components and potential expenses, including maintenance and additional features, stakeholders can create a comprehensive budget that aligns with their goals. As projects evolve, revisiting and adjusting budget estimates will ensure that resources are allocated effectively and that communication with developers remains clear and productive.